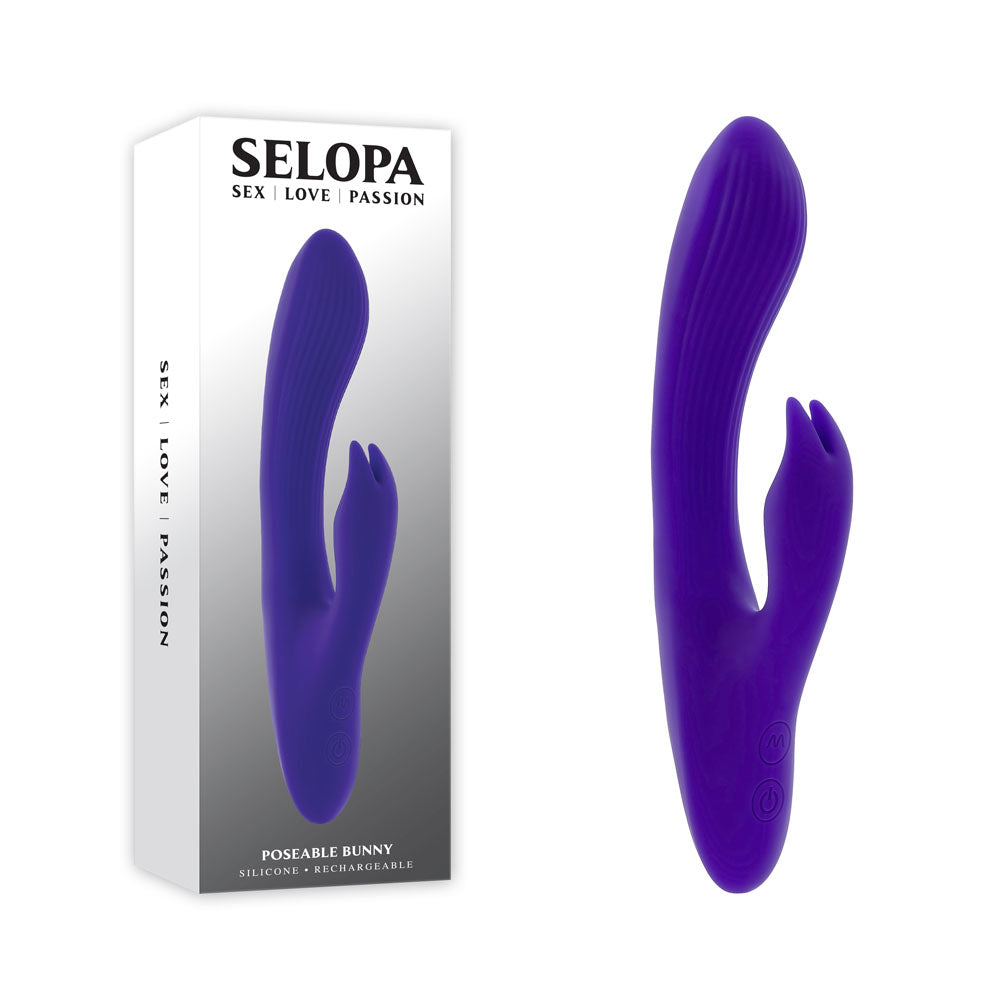
25 Myths Surrounding Male Masturbation

Male masturbation is a natural and healthy aspect of human sexuality, yet it is encumbered by a multitude of myths and stigmas. In this blog, we delve into 25 prevalent misconceptions surrounding male masturbation, shedding light on the cultural, religious, and societal influences that perpetuate these myths. By critically examining each myth, we aim to challenge prevailing attitudes and foster a more informed, inclusive, and sex-positive understanding of male masturbation.
1. Myth: Masturbation is a sinful or immoral act.
Fact: Cultural and religious beliefs have often condemned masturbation as a sinful or immoral act. However, moral judgments surrounding sexual behaviours are subjective and vary across cultures and religious traditions. Masturbation, when practiced consensually and respectfully, is a natural expression of human sexuality and does not carry inherent moral implications.
2. Myth: Masturbation causes physical or mental health problems.
Fact: It is a common misconception that masturbation leads to physical or mental health issues. However, scientific research consistently affirms that masturbation is a normal and safe sexual activity that does not cause harm. In fact, it can offer various health benefits, such as stress reduction, improved sleep, and enhanced mood.
3. Myth: Masturbation leads to sexual weakness or impotence.
Fact: Another prevalent myth is the belief that frequent masturbation can result in sexual weakness or impotence. However, there is no scientific evidence supporting this claim. Sexual difficulties, such as erectile dysfunction, are typically caused by underlying medical or psychological factors, not masturbation itself.
4. Myth: Masturbation is a sign of sexual dissatisfaction in a relationship.
Fact: Masturbation is a personal and individual sexual activity that does not reflect dissatisfaction with a partner. It is important to recognize that sexual satisfaction is multifaceted and can involve both solo and partnered experiences. Masturbation can coexist harmoniously with a healthy and fulfilling sexual relationship.
5. Myth: Masturbation is an addictive behaviour.
Fact: While it is possible for some individuals to develop compulsive sexual behaviours, commonly referred to as sexual addiction or hypersexuality, masturbation itself is not inherently addictive. Masturbation, when practiced in a balanced and consensual manner, is a normal and healthy aspect of human sexuality.
6. Myth: Masturbation causes physical or psychological abnormalities.
Fact: There is no scientific evidence to support the claim that masturbation causes physical or psychological abnormalities. This myth is rooted in unfounded fears and misunderstandings about the nature of sexual pleasure. Masturbation is a natural and personal exploration of one's own body and desires, devoid of any inherent negative consequences.
7. Myth: Masturbation leads to hair loss or baldness.
Fact: The belief that masturbation causes hair loss or baldness is a persistent myth unsupported by scientific evidence. Hair loss is primarily influenced by genetics, hormonal factors, and aging, not sexual activity.
8. Myth: Masturbation reduces fertility or sperm count.
Fact: Masturbation does not decrease fertility or sperm count. Regular ejaculation through masturbation or sexual intercourse is a normal physiological process that helps maintain healthy sperm production. Sperm count and fertility are influenced by various factors unrelated to masturbation.
9. Myth: Masturbation is a waste of sexual energy.
Fact: Masturbation is a healthy way to explore one's sexuality and release sexual tension. It does not waste sexual energy but rather provides an opportunity for self-discovery, stress relief, and personal pleasure.
10. Myth: Masturbation is only for individuals without sexual partners.
Fact: Masturbation is a sexual activity that can be enjoyed by individuals in various relationship statuses. It is not exclusive to those without sexual partners. Masturbation can serve as a means of self-exploration, stress relief, and personal pleasure, regardless of one's relationship status or sexual preferences.
11. Myth: Masturbation is a juvenile or immature behaviour.
Fact: Masturbation is a natural and normal sexual behaviour that is not limited to any specific age group. It is a personal and individual experience that can be practiced throughout one's life. Recognizing the diverse ways in which individuals experience pleasure and explore their bodies is fundamental to fostering a healthy understanding of human sexuality.

12. Myth: Masturbation causes sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Fact: Masturbation, when practiced individually, does not transmit STIs. However, if shared sexual devices or bodily fluids are involved, there may be a risk of transmission. Proper hygiene and safe sex practices should be followed to minimize the risk of STIs.
13. Myth: Masturbation leads to physical weakness or fatigue.
Fact: Masturbation does not cause physical weakness or fatigue. Like any physical activity, it may result in temporary fatigue, but it does not have long-term detrimental effects on physical strength or energy levels.
14. Myth: Masturbation is a substitute for real sex.
Fact: Masturbation and partnered sex are separate but equally valid forms of sexual expression. Masturbation can complement a healthy sexual relationship, but it is not a substitute for intimacy and connection with a partner.
15. Myth: Masturbation is a solitary and isolating activity.
Fact: While masturbation is often practiced alone, it does not necessarily lead to isolation. Masturbation can be integrated into a broader sexual repertoire that includes both solo and partnered activities. In fact, open communication and mutual exploration of self-pleasure can foster intimacy, trust, and connection within a relationship.
16. Myth: Masturbation causes sexual dysfunction.
Fact: Masturbation does not cause sexual dysfunction. In fact, it can help individuals become more familiar with their bodies and enhance sexual function and pleasure.
17. Myth: Masturbation is only for individuals with high sex drives.
Fact: Masturbation is a personal choice and can be enjoyed by individuals with varying sex drives. It provides an opportunity for self-exploration and sexual expression, regardless of one's level of sexual desire.
18. Myth: Masturbation is a sign of deviant or abnormal sexual behaviour.
Fact: Masturbation is a normal and healthy sexual behaviour. It is a common practice across different cultures and has been observed throughout history. Labelling it as deviant or abnormal is based on societal biases and misconceptions.
19. Myth: Masturbation is a male-exclusive activity.
Fact: Masturbation is not limited to males. People of all genders engage in self-pleasure as a natural part of their sexual expression and exploration.
20. Myth: Masturbation causes vision problems.
Fact: There is no scientific evidence to support the claim that masturbation causes vision problems. This myth likely stems from historical misunderstandings and unfounded beliefs.
21. Myth: Masturbation depletes essential nutrients from the body.
Fact: Masturbation does not deplete essential nutrients from the body. Nutrient levels are primarily influenced by overall diet and lifestyle choices, not sexual activity.
22. Myth: Masturbation is a dirty or shameful act.
Fact: Masturbation is a normal and healthy aspect of human sexuality. Feelings of shame or dirtiness surrounding masturbation are often rooted in societal taboos and unfounded judgments.
23. Myth: Masturbation is a form of self-gratification without emotional connection.
Fact: Masturbation can be a self-gratifying experience, but it does not preclude emotional connection. Individuals can experience pleasure and emotional fulfillment through self-pleasure as well as through intimate connections with others.
24. Myth: Masturbation is a sign of sexual inadequacy or inability to satisfy a partner.
Fact: Masturbation is not indicative of sexual inadequacy. It is a personal choice and a way to explore one's own pleasure. It does not imply an inability to satisfy a partner, as sexual satisfaction is a multifaceted and individual experience.
25. Myth: Masturbation is a secretive and hidden behaviour.
Fact: While some individuals may choose to keep their masturbation habits private, it is not inherently secretive or hidden. Open and honest conversations about masturbation can contribute to a more sex-positive and inclusive society.
By debunking these myths and stigmas, we can promote a more accurate and accepting understanding of male masturbation, fostering healthier attitudes towards sexuality and self-exploration.